''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
Biblical account
The life of Solomon is primarily described in 2Chronology
The conventional dates of Solomon's reign are derived from biblical chronology and are set from about 970 to 931 Common Era, BCE. Regarding the Davidic line, Davidic dynasty, to which King Solomon belongs, its chronology can be checked against datable Babylonian and Assyrian records at a few points, and these correspondences have allowed archaeologists to date its kings in a modern framework. According to the most widely used chronology, based on that by Old Testament professor Edwin R. Thiele, the death of Solomon and the division of his kingdom would have occurred in the fall of 931 BCE.Childhood
Solomon was born inSuccession and administration
 According to the First Book of Kings, when David was old, "he could not get warm". "So they sought a beautiful young woman throughout all the territory of Israel, and found Abishag the Shunamitism, Shunamite, and brought her to the king. The young woman was very beautiful, and she was of service to the king and attended to him, but the king knew her not."
While David was in this state, court factions were maneuvering for power. David's heir apparent, Adonijah, acted to have himself declared king, but was outmaneuvered by Bathsheba and the prophet Nathan (Prophet), Nathan, who convinced David to proclaim Solomon king according to his earlier promise (not recorded elsewhere in the biblical narrative), despite Solomon's being younger than his brothers.
Solomon, as instructed by David, began his reign with an extensive purge, including his father's chief general, Joab, among others, and further consolidated his position by appointing friends throughout the administration, including in religious positions as well as in civic and military posts. It is said that Solomon ascended to the throne when he was only about fifteen.
Solomon greatly expanded his military strength, especially the cavalry and chariot arms. He founded numerous colonies, some of which doubled as trading posts and military outposts.
Trade relationships were a focus of his administration. In particular he continued his father's very profitable relationship with the Phoenician king Hiram I of Tyre (see 'wealth' below); they sent out joint expeditions to the lands of Tarshish and Ophir to engage in the trade of luxury products, importing gold, silver, sandalwood, pearls, ivory, apes and peacocks. Solomon is considered the most wealthy of the Israelite kings named in the Bible.
According to the First Book of Kings, when David was old, "he could not get warm". "So they sought a beautiful young woman throughout all the territory of Israel, and found Abishag the Shunamitism, Shunamite, and brought her to the king. The young woman was very beautiful, and she was of service to the king and attended to him, but the king knew her not."
While David was in this state, court factions were maneuvering for power. David's heir apparent, Adonijah, acted to have himself declared king, but was outmaneuvered by Bathsheba and the prophet Nathan (Prophet), Nathan, who convinced David to proclaim Solomon king according to his earlier promise (not recorded elsewhere in the biblical narrative), despite Solomon's being younger than his brothers.
Solomon, as instructed by David, began his reign with an extensive purge, including his father's chief general, Joab, among others, and further consolidated his position by appointing friends throughout the administration, including in religious positions as well as in civic and military posts. It is said that Solomon ascended to the throne when he was only about fifteen.
Solomon greatly expanded his military strength, especially the cavalry and chariot arms. He founded numerous colonies, some of which doubled as trading posts and military outposts.
Trade relationships were a focus of his administration. In particular he continued his father's very profitable relationship with the Phoenician king Hiram I of Tyre (see 'wealth' below); they sent out joint expeditions to the lands of Tarshish and Ophir to engage in the trade of luxury products, importing gold, silver, sandalwood, pearls, ivory, apes and peacocks. Solomon is considered the most wealthy of the Israelite kings named in the Bible.
Wisdom
 Solomon was the biblical king most famous for his wisdom. In 1Kings he sacrificed to God, and God later appeared to him in a dream, asking what Solomon wanted from God. Solomon asked for wisdom in order to better rule and guide his people. Pleased, God personally answered Solomon's prayer, promising him great wisdom because he did not ask for self-serving rewards like long life or the death of his enemies.
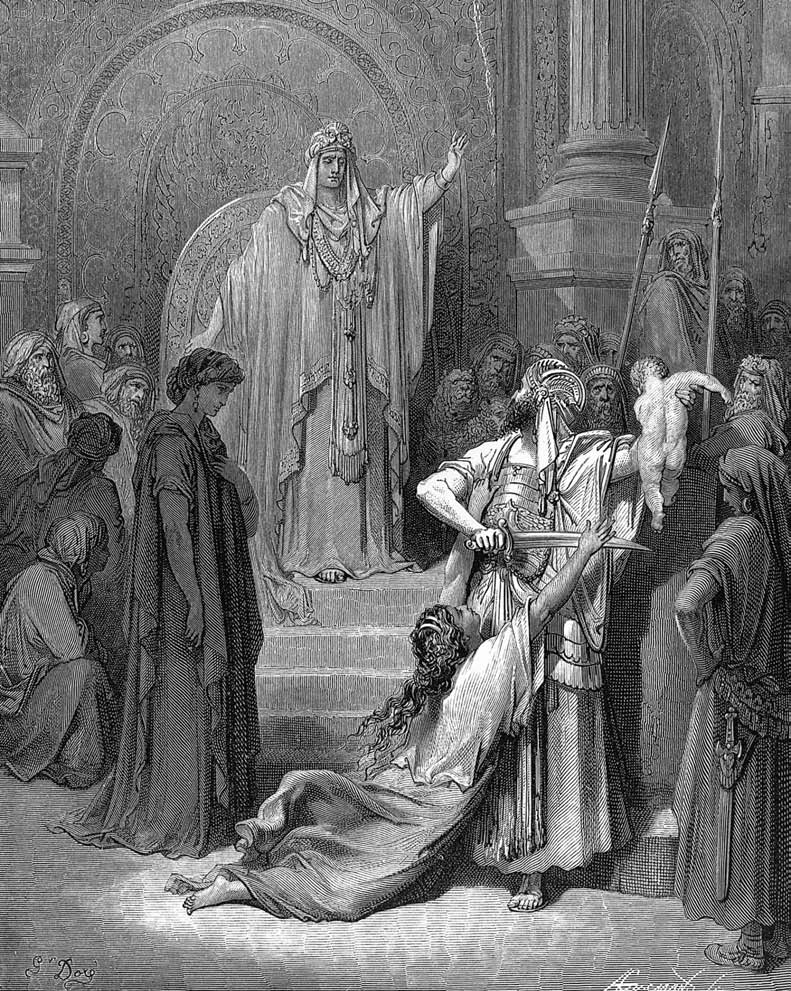
Perhaps the best known story of his wisdom is the Judgment of Solomon; two women each lay claim to being the mother of the same child. Solomon easily resolved the dispute by commanding the child to be cut in half and shared between the two. One woman promptly renounced her claim, proving that she would rather give the child up than see it killed. Solomon declared the woman who showed compassion to be the true mother, entitled to the whole child.
Solomon was traditionally considered the author of several biblical books, "including not only the collections of Book of Proverbs, Proverbs, but also of Ecclesiastes and the Song of Solomon and the later apocryphal book the Wisdom of solomon, Wisdom of Solomon."
Solomon was the biblical king most famous for his wisdom. In 1Kings he sacrificed to God, and God later appeared to him in a dream, asking what Solomon wanted from God. Solomon asked for wisdom in order to better rule and guide his people. Pleased, God personally answered Solomon's prayer, promising him great wisdom because he did not ask for self-serving rewards like long life or the death of his enemies.
Perhaps the best known story of his wisdom is the Judgment of Solomon; two women each lay claim to being the mother of the same child. Solomon easily resolved the dispute by commanding the child to be cut in half and shared between the two. One woman promptly renounced her claim, proving that she would rather give the child up than see it killed. Solomon declared the woman who showed compassion to be the true mother, entitled to the whole child.
Solomon was traditionally considered the author of several biblical books, "including not only the collections of Book of Proverbs, Proverbs, but also of Ecclesiastes and the Song of Solomon and the later apocryphal book the Wisdom of solomon, Wisdom of Solomon."
Wealth
 According to the Hebrew Bible, the United Monarchy, ancient Kingdom of Israel gained its highest splendour and wealth during Solomon's reign of 40 years. In a single year, according to , Solomon collected tribute amounting to 666 talent (weight), talents (18,125 kilograms) of gold. Solomon is described as surrounding himself with all the luxuries and the grandeur of an Eastern world, Eastern monarch, and his government prospered. He entered into an alliance with Hiram I, king of Tyre (Lebanon), Tyre, who in many ways greatly assisted him in his numerous undertakings.
According to the Hebrew Bible, the United Monarchy, ancient Kingdom of Israel gained its highest splendour and wealth during Solomon's reign of 40 years. In a single year, according to , Solomon collected tribute amounting to 666 talent (weight), talents (18,125 kilograms) of gold. Solomon is described as surrounding himself with all the luxuries and the grandeur of an Eastern world, Eastern monarch, and his government prospered. He entered into an alliance with Hiram I, king of Tyre (Lebanon), Tyre, who in many ways greatly assisted him in his numerous undertakings.
Construction projects
 For some years before his death, David was engaged in collecting materials for building a temple in Jerusalem as a permanent home for
For some years before his death, David was engaged in collecting materials for building a temple in Jerusalem as a permanent home for 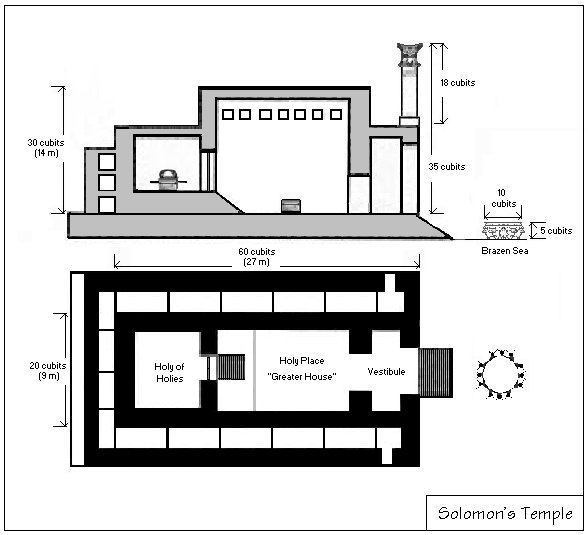 Solomon's Throne, Solomon's throne is said to have been spectacularly opulent and possessed moving parts, making it one of the earliest mechanical devices in history. Solomon also constructed great water works for the city, and the Millo (Septuagint, ''Acra'') for the defense of the city. However, excavations of Jerusalem have discovered no monumental architecture from the era, and no remains of either the Temple or Solomon's palace have been found.
Solomon is also described as rebuilding cities elsewhere in Israel, creating the port of Ezion-Geber, and constructing Palmyra in the wilderness as a commercial depot and military outpost. Although the location of the port of Ezion-Geber is known, no remains have ever been found. More archaeological success has been achieved with the major cities Solomon is said to have strengthened or rebuilt, for example, Tel Hazor, Hazor, Tel Megiddo, Megiddo and Gezer. These all have substantial ancient remains, including impressive six-chambered gates, and ashlar palaces; however it is no longer the scholarly consensus that these structures date to the time, according to the Bible, when Solomon ruled.
According to the Bible, during Solomon's reign, Israel enjoyed great commercial prosperity, with extensive traffic being carried on by land with Tyre (Lebanon), Tyre, Egypt, and Arabia, and by sea with Tarshish, Ophir, and South India.
Solomon's Throne, Solomon's throne is said to have been spectacularly opulent and possessed moving parts, making it one of the earliest mechanical devices in history. Solomon also constructed great water works for the city, and the Millo (Septuagint, ''Acra'') for the defense of the city. However, excavations of Jerusalem have discovered no monumental architecture from the era, and no remains of either the Temple or Solomon's palace have been found.
Solomon is also described as rebuilding cities elsewhere in Israel, creating the port of Ezion-Geber, and constructing Palmyra in the wilderness as a commercial depot and military outpost. Although the location of the port of Ezion-Geber is known, no remains have ever been found. More archaeological success has been achieved with the major cities Solomon is said to have strengthened or rebuilt, for example, Tel Hazor, Hazor, Tel Megiddo, Megiddo and Gezer. These all have substantial ancient remains, including impressive six-chambered gates, and ashlar palaces; however it is no longer the scholarly consensus that these structures date to the time, according to the Bible, when Solomon ruled.
According to the Bible, during Solomon's reign, Israel enjoyed great commercial prosperity, with extensive traffic being carried on by land with Tyre (Lebanon), Tyre, Egypt, and Arabia, and by sea with Tarshish, Ophir, and South India.
Wives and concubines
 According to the biblical account, Solomon had 700 wives and 300 concubines. The wives were described as foreign princesses, including Pharaoh's daughter (wife of Solomon), Pharaoh's daughter and women of Moab, Ammon, Edom, Sidon and of the Hittites. His marriage to Pharaoh's daughter appears to have cemented a political alliance with Egypt, whereas he clung to his other wives and concubines "in love". The only wife mentioned by name is Naamah (wife of Solomon), Naamah the Ammonites (people), Ammonite, mother of Solomon's successor,
According to the biblical account, Solomon had 700 wives and 300 concubines. The wives were described as foreign princesses, including Pharaoh's daughter (wife of Solomon), Pharaoh's daughter and women of Moab, Ammon, Edom, Sidon and of the Hittites. His marriage to Pharaoh's daughter appears to have cemented a political alliance with Egypt, whereas he clung to his other wives and concubines "in love". The only wife mentioned by name is Naamah (wife of Solomon), Naamah the Ammonites (people), Ammonite, mother of Solomon's successor, Relationship with Queen of Sheba
In a brief, unelaborated, and enigmatic passage, the Hebrew Bible describes how the fame of Solomon's wisdom and wealth reached even the far-off Queen of Sheba. The queen is described as visiting with gifts including gold, spices and precious stones. When Solomon gave her "all her desire, whatsoever she asked", she left satisfied1 Kings 10:10
. Whether the passage is simply to provide a brief foreign witness of Solomon's wealth and wisdom, or whether the visit is meant to have more significance, is unknown; nevertheless the Queen of Sheba has become the subject of numerous stories. Sheba is typically identified as Sabaeans, Saba, a nation once spanning the Red Sea on the coasts of what are now Eritrea, Somalia, Ethiopia and Yemen, in Arabia Felix; although other sources place it in the area of what is now northern Ethiopia and Eritrea. In a Rabbinical account (e.g. Targum Sheni, s:Translation:Colloquy of the Queen of Sheba, Colloquy of the Queen of Sheba), Solomon was accustomed to ordering animals to dance before him (a power granted by God), and upon summoning the mountain-cock or hoopoe (Aramaic name: ''nagar tura''), the bird told him it had discovered a land in the east, rich in gold, silver, and plants, whose capital was called ''Kitor'' and whose ruler was the Queen of Sheba. Solomon then sent the bird to request the queen's visit. An Ethiopian account from the 14th century (''Kebra Nagast'') maintains that the Queen of Sheba had sexual relations with King Solomon and gave birth beside the Mai Bella stream in the province of Hamasien, Eritrea. The Ethiopian tradition has a Queen of Sheba#Ethiopian, detailed account of the affair. The child was a son who became Menelik I, King of Kingdom of Axum, Axum, and founded a Solomonic dynasty, dynasty that would reign as the Jewish, then Christian, Empire of Ethiopia which lasted 2900 years until Haile Selassie was overthrown in 1974. Menelik was said to be a practicing Jew who was given a replica of the Ark of the Covenant by King Solomon; and, moreover, that the original Ark was switched and went to Axum with him and his mother, and is still there, guarded by a single dedicated priest. The claim of such a lineage and of possession of the Ark was an important source of legitimacy and prestige for the Ethiopian monarchy through the centuries, and had important and lasting effects on Culture of Ethiopia, Ethiopian culture. The Ethiopian government and church deny all requests to view the alleged ark. Some classical-era Rabbis, attacking Solomon's moral character, have claimed instead that the child was an ancestor of Nebuchadnezzar II, who destroyed Solomon's temple some 300 years later.
Sins and punishment
 Jewish scribes say that Solomon's teacher was Shimei (son of Gera), and while he lived, he prevented Solomon from marrying foreign wives. The Talmud says at Ber. 8a: "For as long as Shimei the son of Gera was alive Solomon did not marry the daughter of Pharaoh" (see also Midrash Tehillim to Ps. 3:1). Solomon's execution of Shimei was his first descent into sin.
According to Solomon's "wives turned his heart after other gods", their own national deities, to whom Solomon built temples, thus incurring divine anger and retribution in the form of the division of the kingdom after Solomon's death ().
describes Solomon's descent into idolatry, particularly his turning after Ashtoreth, the goddess of the Sidonians, and after Milcom, the god of the Ammonites. In , a king is commanded not to multiply horses or wives, neither greatly multiply to himself gold or silver. Solomon sinned in all three of these areas. In addition to his wives, he collected 666 (number), 666 talent (measurement), talents of gold each year (), a huge amount for a small nation like Israel. He gathered multitudes of horses and chariots from as far as Egypt, and as warns, took Israel back to Egypt in spirit.
Jewish scribes say that Solomon's teacher was Shimei (son of Gera), and while he lived, he prevented Solomon from marrying foreign wives. The Talmud says at Ber. 8a: "For as long as Shimei the son of Gera was alive Solomon did not marry the daughter of Pharaoh" (see also Midrash Tehillim to Ps. 3:1). Solomon's execution of Shimei was his first descent into sin.
According to Solomon's "wives turned his heart after other gods", their own national deities, to whom Solomon built temples, thus incurring divine anger and retribution in the form of the division of the kingdom after Solomon's death ().
describes Solomon's descent into idolatry, particularly his turning after Ashtoreth, the goddess of the Sidonians, and after Milcom, the god of the Ammonites. In , a king is commanded not to multiply horses or wives, neither greatly multiply to himself gold or silver. Solomon sinned in all three of these areas. In addition to his wives, he collected 666 (number), 666 talent (measurement), talents of gold each year (), a huge amount for a small nation like Israel. He gathered multitudes of horses and chariots from as far as Egypt, and as warns, took Israel back to Egypt in spirit.
 According to and , it was because of these sins that the Lord punished Solomon by removing most of the tribes of Israel from rule by Solomon's house.
According to and , it was because of these sins that the Lord punished Solomon by removing most of the tribes of Israel from rule by Solomon's house.
Enemies
Near the end of his life, Solomon was beset by several enemies, including Hadad the Edomite, Hadad of Edom, Rezon the Syrian, Rezon of Zobah, and his own official Jeroboam of the tribe of Ephraim.Death, succession of Rehoboam, and kingdom division
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
Apocryphal or deuterocanonical texts
Rabbinical tradition attributes the ''Wisdom of Solomon'' (included within the Septuagint) to Solomon, although this book was probably written in the 2nd century BCE. In this work, Solomon is portrayed as an astronomer. Other books of wisdom poetry such as the ''Odes of Solomon'' and the ''Psalms of Solomon'' also bear his name. The Jewish historian Eupolemus, who wrote about 157 BCE, included copies of apocryphal letters exchanged between Solomon and the kings of Egypt and Tyre (Lebanon), Tyre. The Gnostic ''Apocalypse of Adam'', which may date to the 1st or 2nd century, refers to a legend in which Solomon sends out an army of demons to seek a virgin who had fled from him, perhaps the earliest surviving mention of the later common tale that Solomon controlled demons and made them his slaves. This tradition of Solomon's control over demons appears fully elaborated in the early pseudoepigraphical work called the ''Historicity
As with most biblical personages in the middle era of Israelite society, the historicity of Solomon is hotly debated. Current consensus states that regardless of whether or not a man named Solomon truly reigned as king over the Judean hills in the tenth century BCE, the Biblical descriptions of his apparent empire's lavishness is almost surely an anachronistic exaggeration. As for Solomon himself, scholars on both the Biblical maximalism, maximalist and Biblical minimalism, minimalist sides of the spectrum of biblical archeology generally agree that he probably existed. However, a historically accurate picture of the Davidic king is difficult to construct. According to some archaeologists, Solomon could have only been the monarch or chieftain of Judah, and that the northern kingdom was a separate development. Such positions have been criticized by other archaeologists and scholars, who argue that a united monarchy did exist in the 10th century BC, while agreeing that the biblical account contains exaggerations.Arguments against biblical description
 Historical evidence of King Solomon other than the biblical accounts has been so minimal that some scholars have understood the period of his reign as a 'Dark Age' (Muhly 1998). The first-century Roman Jews, Romano-Jewish scholar Josephus in ''Against Apion'', citing Tyre, Lebanon, Tyrian court records and Menander of Ephesus, Menander, gives a specific year during which King Hiram I of Tyre sent materials to Solomon for the construction of the Solomon's Temple, Temple. However, no material evidence indisputably of Solomon's reign has been found. Yigael Yadin's excavations at Tel Hazor, Hazor, Tel Megiddo, Megiddo, Beit Shean and Gezer uncovered structures that he and others have argued date from Solomon's reign, but others, such as Israel Finkelstein and Neil Silberman, argue that they should be dated to the Omrides, Omride period, more than a century after Solomon.
According to Finkelstein and Silberman, authors of ''The Bible Unearthed: Archaeology's New Vision of Ancient Israel and the Origin of Its Sacred Texts'', at the time of the kingdoms of David and Solomon, Jerusalem was populated by only a few hundred residents or less, which is insufficient for an empire stretching from the Euphrates to Eilath#Biblical references, Eilath. According to ''The Bible Unearthed'', archaeological evidence suggests that the kingdom of Israel at the time of Solomon was little more than a small city state, and so it is implausible that Solomon received tribute as large as 666 talent (weight), talents of gold per year. Although both Finkelstein and Silberman accept that David and Solomon were real inhabitants of Judah about the 10th century BCE, they claim that the earliest independent reference to the Kingdom of Israel is about 890 BCE, and for Judah about 750 BCE. They suggest that because of religious prejudice, the authors of the Bible suppressed the achievements of the Omrides (whom the Hebrew Bible describes as being polytheist), and instead pushed them back to a supposed golden age of Judaism and monotheists, and devotees of Yahweh. Some biblical minimalism, Biblical minimalists like Thomas L. Thompson go further, arguing that Jerusalem became a city and capable of being a state capital only in the mid-7th century. Likewise, Finkelstein and others consider the claimed size of Solomon's temple implausible.
Historical evidence of King Solomon other than the biblical accounts has been so minimal that some scholars have understood the period of his reign as a 'Dark Age' (Muhly 1998). The first-century Roman Jews, Romano-Jewish scholar Josephus in ''Against Apion'', citing Tyre, Lebanon, Tyrian court records and Menander of Ephesus, Menander, gives a specific year during which King Hiram I of Tyre sent materials to Solomon for the construction of the Solomon's Temple, Temple. However, no material evidence indisputably of Solomon's reign has been found. Yigael Yadin's excavations at Tel Hazor, Hazor, Tel Megiddo, Megiddo, Beit Shean and Gezer uncovered structures that he and others have argued date from Solomon's reign, but others, such as Israel Finkelstein and Neil Silberman, argue that they should be dated to the Omrides, Omride period, more than a century after Solomon.
According to Finkelstein and Silberman, authors of ''The Bible Unearthed: Archaeology's New Vision of Ancient Israel and the Origin of Its Sacred Texts'', at the time of the kingdoms of David and Solomon, Jerusalem was populated by only a few hundred residents or less, which is insufficient for an empire stretching from the Euphrates to Eilath#Biblical references, Eilath. According to ''The Bible Unearthed'', archaeological evidence suggests that the kingdom of Israel at the time of Solomon was little more than a small city state, and so it is implausible that Solomon received tribute as large as 666 talent (weight), talents of gold per year. Although both Finkelstein and Silberman accept that David and Solomon were real inhabitants of Judah about the 10th century BCE, they claim that the earliest independent reference to the Kingdom of Israel is about 890 BCE, and for Judah about 750 BCE. They suggest that because of religious prejudice, the authors of the Bible suppressed the achievements of the Omrides (whom the Hebrew Bible describes as being polytheist), and instead pushed them back to a supposed golden age of Judaism and monotheists, and devotees of Yahweh. Some biblical minimalism, Biblical minimalists like Thomas L. Thompson go further, arguing that Jerusalem became a city and capable of being a state capital only in the mid-7th century. Likewise, Finkelstein and others consider the claimed size of Solomon's temple implausible.
Arguments in favour of biblical description
 André Lemaire states in ''Ancient Israel: From Abraham to the Roman Destruction of the Temple'' that the principal points of the biblical tradition of Solomon are generally trustworthy, although elsewhere he writes that he could find no substantiating archaeological evidence that supports the Queen of Sheba's visit to king Solomon, saying that the earliest records of trans-Arabian caravan voyages from Tayma and Sheba unto the Middle-Euphrates etc. occurred in the mid-8th century BCE, placing a possible visit from the Queen of Sheba to Jerusalem around this time—some 250 years later than the timeframe traditionally given for king Solomon's reign. Seventeen years later, traces of cinnamon were found in Phoenician clay flasks from three small sites in the Israeli coastal plain dating from the 10th century BCE. The authors suggested that trade routes with South Asia existed much earlier than previously thought.
Kenneth Kitchen argues that Solomon ruled over a comparatively wealthy "mini-empire", rather than a small city-state, and considers 666 gold talents a modest amount of money. Kitchen calculates that over 30 years, such a kingdom might have accumulated up to 500 tons of gold, which is small compared to other examples, such as the 1,180 tons of gold that Alexander the Great took from Susa. Similarly, Kitchen and others consider the temple of Solomon a reasonable and typically sized structure for the region at the time. Dever states "that we now have direct Bronze and Iron Age parallels for every feature of the 'Solomonic temple' as described in the Hebrew Bible".
André Lemaire states in ''Ancient Israel: From Abraham to the Roman Destruction of the Temple'' that the principal points of the biblical tradition of Solomon are generally trustworthy, although elsewhere he writes that he could find no substantiating archaeological evidence that supports the Queen of Sheba's visit to king Solomon, saying that the earliest records of trans-Arabian caravan voyages from Tayma and Sheba unto the Middle-Euphrates etc. occurred in the mid-8th century BCE, placing a possible visit from the Queen of Sheba to Jerusalem around this time—some 250 years later than the timeframe traditionally given for king Solomon's reign. Seventeen years later, traces of cinnamon were found in Phoenician clay flasks from three small sites in the Israeli coastal plain dating from the 10th century BCE. The authors suggested that trade routes with South Asia existed much earlier than previously thought.
Kenneth Kitchen argues that Solomon ruled over a comparatively wealthy "mini-empire", rather than a small city-state, and considers 666 gold talents a modest amount of money. Kitchen calculates that over 30 years, such a kingdom might have accumulated up to 500 tons of gold, which is small compared to other examples, such as the 1,180 tons of gold that Alexander the Great took from Susa. Similarly, Kitchen and others consider the temple of Solomon a reasonable and typically sized structure for the region at the time. Dever states "that we now have direct Bronze and Iron Age parallels for every feature of the 'Solomonic temple' as described in the Hebrew Bible".
Middle way
Some scholars have charted a middle path between minimalist scholars like Finkelstein, Silberman, and Philip Davies (who believes that "Solomon is a totally invented character") and maximalist scholars like Dever, Lemaire and Kitchen. For instance, the archaeologist Avraham Faust has argued that biblical depictions of Solomon date to later periods and do overstate his wealth, buildings, and kingdom, but that Solomon did have an acropolis and ruled over a polity larger than Jerusalem. In particular, his archaeological research in regions near Jerusalem, like Sharon, finds commerce too great not to be supported by a polity and such regions probably were ruled loosely by Jerusalem. Scholars like Lester Grabbe also believe that there must have been a ruler in Jerusalem during this period and that he likely built a temple, although the town was quite small. William G. Dever argues that Solomon only reigned over Israel and did build a temple, but that descriptions of his lavishness and the other conquests are strongly exaggerated.Archaeology
General observations
The archaeological remains that are considered to date from the time of Solomon are notable for the fact that Canaanite material culture appears to have continued unabated; there is a distinct lack of magnificent empire, or cultural development—indeed comparing pottery from areas traditionally assigned to Israel with that of the Philistines points to the latter having been significantly more sophisticated. However, there is a lack of physical evidence of its existence, despite some archaeological work in the area. This is not unexpected because the area was devastated by the Babylonians, then rebuilt and destroyed several times.Temple Mount in Jerusalem
Little archaeological excavation has been done around the area known as the Temple Mount, in what is thought to be the foundation of Solomon's Temple, because attempts to do so are met with protests by the Jerusalem Islamic Waqf, Muslim authorities.Precious metals from Tarshish
The biblical passages that understand Tarshish as a source of King Solomon's great wealth in metals—especially silver, but also gold, tin and iron (Ezekiel 27)—were linked to archaeological evidence from silver-hoards found in Phoenicia in 2013. The metals from Tarshish were reportedly obtained by Solomon in partnership with King Hiram of Phoenician Tyre (Isaiah 23) and the fleets of Tarshish and ships that sailed in their service. The silver hoards provide the first recognized material evidence that agrees with the ancient texts concerning Solomon's kingdom and his wealth (see 'wealth' below). Possible evidence for the described wealth of Solomon and his kingdom was discovered in ancient silver hoards, which were found in Israel and Phoenicia and recognized for their importance in 2003. The evidence from the hoards shows that the Levant was a center of wealth in precious metals during the reigns of Solomon and Hiram, and matches the texts that say the trade extended from Asia to the Atlantic Ocean.Biblical criticism: Solomon's religiosity
From a critical point of view, Solomon's building of a temple for Yahweh should not be considered an act of particular devotion to Yahweh because Solomon is also described as building places of worship for a number of other deities. Some scholars and historians argue that the passages, such as his dedication prayer (), that describe Solomon's apparent initial devotion to Yahweh were written much later, after Jerusalem had become the religious centre of the kingdom, replacing locations such as Shiloh (Biblical city), Shiloh and Bethel. Earlier historians maintain that there is evidence that these passages in Kings are derived from official court records at the time of Solomon and from other writings of that time that were incorporated into the canonical books of Kings. More recent scholars believe that passages such as these in the Books of Kings were not written by the same authors who wrote the rest of the text, instead probably by the Deuteronomist.Religious views
Judaism
King Solomon sinned by acquiring many foreign wives and horses because he thought he knew the reason for the biblical prohibition and thought it did not apply to him. When King Solomon married the daughter of the Egyptian Pharaoh, a sandbank formed which eventually formed the "great nation of Rome"—the nation that destroyed the Second Temple (Herod's Temple). Solomon gradually lost more and more prestige until he became like a commoner. Some say he regained his status while others say he did not. In the end, however, he is regarded as a righteous king and is especially praised for his diligence in building the Temple. King Josiah was also said to have had the Ark of the Covenant, Aaron's rod, vial of manna and the anointing oil placed within a hidden chamber which had been built by King Solomon The Seder Olam Rabba holds that Solomon's reign was not in 1000 BCE, but rather in the 9th century BCE, during which time he built the First Temple in 832 BCE. However, the 1906 Jewish Encyclopedia gives the more common date of "971 to 931 BCE".Christianity
Islam
Baháʼí Faith
In the Baháʼí Faith, Solomon is regarded as one of the lesser prophets along with David, Isaiah, Jeremiah, Ezekiel, along with others. Baháʼís see Solomon as a prophet who was sent by God to address the issues of his time. Baha'ullah wrote about Solomon in the ''Hidden Words''. He also mentions Solomon in the ''Tablet of Wisdom'', where he is depicted as a contemporary of Pythagoras.Legends
''One Thousand and One Nights''
A well-known story in the collection ''One Thousand and One Nights'' describes a genie who had displeased King Solomon and was punished by being locked in a bottle and thrown into the sea. Since the bottle was sealed with Solomon's seal, the genie was helpless to free himself, until he was freed many centuries later by a fisherman who discovered the bottle. In other stories from the ''One Thousand and One Nights'', protagonists who had to leave their homeland and travel to the unknown places of the world saw signs which proved that Solomon had already been there. Sometimes, protagonists discovered words of Solomon that were intended to help those who were lost and had unluckily reached those forbidden and deserted places.Angels and magic
According to the Rabbinical literature, on account of his modest request for wisdom only, Solomon was rewarded with riches and an unprecedented glorious realm, which extended over the upper world inhabited by the angels and over the whole of the terrestrial globe with all its inhabitants, including all the beasts, fowl, and reptiles, as well as the demons and spirits. His control over the demons, spirits, and animals augmented his splendor, the demons bringing him precious stones, besides water from distant countries to irrigate his exotic plants. The beasts and fowl of their own accord entered the kitchen of Solomon's palace, so that they might be used as food for him, and extravagant meals for him were prepared daily by each of his 700 wives and 300 concubines, with the thought that perhaps the king would feast that day in her house.Seal of Solomon
The Seal of Solomon or Ring of Solomon is the legendary Seal (emblem), signet ring attributed to the Israelites, Israelite king Solomon in medieval mystical traditions, from which it developed in parallel within Jewish mysticism, Sufism, Islamic mysticism and Western esotericism, Western occultism. It is the predecessor to the Star of David, the contemporary cultural and religious symbol of the Jews, Jewish people. It was often depicted in the shape of either a pentagram or a hexagram. In religious lore, the ring is described as having given Solomon the power to command the supernatural and also the ability to speak with animals. Due to the proverbial wisdom of Solomon, it came to be seen as an amulet or talisman, or a symbol or character in Medieval European magic, medieval magic and Renaissance magic, Occult, occultism, and alchemy.Solomon and Asmodeus
One legend concerning Asmodeus (see: s:Translation:The Story of King Solomon and Ashmedai, The Story of King Solomon and Ashmedai) goes on to state that Solomon one day asked Asmodeus what could make demons powerful over man, and Asmodeus asked to be freed and given the ring so that he could demonstrate; Solomon agreed but Asmodeus threw the ring into the sea and it was swallowed by a fish. Asmodeus then swallowed the king, stood up fully with one wing touching heaven and the other earth, and spat out Solomon to a distance of 400 miles. The Rabbis claim this was a divine punishment for Solomon's having failed to follow three divine commands, and Solomon was forced to wander from city to city, until he eventually arrived in an Ammonites (people), Ammonite city where he was forced to work in the king's kitchens. Solomon gained a chance to prepare a meal for the Ammonite king, which the king found so impressive that the previous cook was sacked and Solomon put in his place; the king's daughter, Naamah (wife of Solomon), Naamah, subsequently fell in love with Solomon, but the family (thinking Solomon a commoner) disapproved, so the king decided to kill them both by sending them into the desert. Solomon and the king's daughter wandered the desert until they reached a coastal city, where they bought a fish to eat, which just happened to be the one which had swallowed the magic ring. Solomon was then able to regain his throne and expel Asmodeus. The element of a ring thrown into the sea and found back in a fish's belly also appeared in Herodotus' account of Polycrates, the tyrant of Samos (c. 538–522 BCE). In another familiar version of the legend of the Seal of Solomon, Asmodeus disguises himself. In some myths, he's disguised as King Solomon himself. The concealed Asmodeus tells travelers who have ventured up to King Solomon's grand lofty palace that the Seal of Solomon was thrown into the sea. He then convinces them to plunge in and attempt to retrieve it, for if they do they would take the throne as king.Artifacts
Other magical items attributed to Solomon are key of Solomon, his key and his Table. The latter was said to be held in Toledo, Spain during Visigoth rule and was part of the loot taken by Tarik ibn Ziyad during the Umayyad Conquest of Iberia, according to Ibn Abd-el-Hakem's ''History of the Conquest of Spain''. The former appears in the title of the Lesser Key of Solomon, a grimoire whose Frame story, framing story is Solomon capturing demons using his ring, and forcing them to explain themselves to him. In ''The Book of Deadly Names'', purportedly translated from Arabic manuscripts found hidden in a building in Spain, the "King of the Jinn" Fiqitush brings 72 jinn before King Solomon to confess their corruptions and places of residence. Fiqitush tells King Solomon the recipes for curing such corruptions as each evil jinn confesses.Angels
Angels also helped Solomon in building the Temple, though not by choice. The edifice was, according to rabbinical legend, miraculously constructed throughout, the large heavy stones rising and settling in their respective places of themselves. The general opinion of the Rabbis is that Solomon hewed the stones by means of a ''Solomon's Shamir, shamir'', a mythical worm whose mere touch cleft rocks. According to Midrash Tehillim, the shamir was brought from paradise by Solomon's eagle; but most of the rabbis state that Solomon was informed of the worm's haunts by Asmodeus. The shamir had been entrusted by the prince of the sea to the mountain rooster alone, and the rooster had sworn to guard it well, but Solomon's men found the bird's nest, and covered it with glass. When the bird returned, it used the shamir to break the glass, whereupon the men scared the bird, causing it to drop the worm, which the men could then bring to Solomon.In the Kabbalah
Early adherents of the Kabbalah portray Solomon as having sailed through the air on a throne of light placed on an eagle, which brought him near the heavenly gates as well as to the dark mountains behind which the fallen angels ''Uzza'' and ''Azzazel'' were chained; the eagle would rest on the chains, and Solomon, using the magic ring, would compel the two angels to reveal every mystery he desired to know.The palace without entrance
According to one legend, while traveling magically, Solomon noticed a magnificent palace to which there appeared to be no entrance. He ordered the demons to climb to the roof and see if they could discover any living being within the building but they found only an eagle, which said that it was 700 years old, but that it had never seen an entrance. An elder brother of the eagle, 900 years old, was then found, but it also did not know the entrance. The eldest brother of these two birds, which was 1,300 years old, then declared it had been informed by its father that the door was on the west side, but that it had become hidden by sand drifted by the wind. Having discovered the entrance, Solomon found an idol inside that had in its mouth a silver tablet saying in Greek (a language not thought by modern scholars to have existed 1000 years before the time of Solomon) that the statue was of ''Shaddad, the son of 'Ad'', and that it had ''reigned over a million cities, rode on a million horses, had under it a million vassals and slew a million warriors'', yet it could not resist the death (personification), angel of death.Throne
 Solomon's throne is described at length in Targum Sheni, which is compiled from three different sources, and in two later Midrash. According to these, there were on the steps of the throne twelve golden lions, each facing a golden eagle. There were six steps to the throne, on which animals, all of gold, were arranged in the following order: on the first step a lion opposite an ox; on the second, a wolf opposite a sheep; on the third, a tiger opposite a camel; on the fourth, an eagle opposite a peacock, on the fifth, a cat opposite a cock; on the sixth, a sparrow-hawk opposite a dove. On the top of the throne was a dove holding a sparrow-hawk in its claws, symbolizing the dominion of Israel over the Gentiles. The first midrash claims that six steps were constructed because Solomon foresaw that six kings would sit on the throne, namely, Solomon,
Solomon's throne is described at length in Targum Sheni, which is compiled from three different sources, and in two later Midrash. According to these, there were on the steps of the throne twelve golden lions, each facing a golden eagle. There were six steps to the throne, on which animals, all of gold, were arranged in the following order: on the first step a lion opposite an ox; on the second, a wolf opposite a sheep; on the third, a tiger opposite a camel; on the fourth, an eagle opposite a peacock, on the fifth, a cat opposite a cock; on the sixth, a sparrow-hawk opposite a dove. On the top of the throne was a dove holding a sparrow-hawk in its claws, symbolizing the dominion of Israel over the Gentiles. The first midrash claims that six steps were constructed because Solomon foresaw that six kings would sit on the throne, namely, Solomon, Freemasonry
Masonic ritual and symbolism, Masonic rituals refer to King Solomon and the building of his Temple. Masonic Temples, where a Masonic Lodge meets, are an allegory, allegorical reference to King Solomon's Temple.Places
The Solomon Islands, a country and archipelago in Melanesia, were named for King Solomon by the Spanish navigator Álvaro de Mendaña, who became the first European to see the islands in 1568.In literature, art, and music
Literature
* In H. Rider Haggard's ''King Solomon's Mines'' (1885) the protagonists discover multiple settings said to have belonged to or to have been built at the request of King Solomon, such as 'Solomon's Great Road' and the mines themselves. Also, the two mountains which form the entrance to Kukuana Land (where the mines are located in the novel) are referred to as 'Sheba's Breasts' which could be an allusion to the Queen of Sheba, with whom King Solomon had a relationship, or Solomon's mother, who was named Bathsheba. When in the mines, the characters also contemplate what must have occurred to prevent King Solomon from returning to retrieve the massive amounts of diamonds, gold and ivory tusks that were found buried in his great 'Treasure Chamber'. * In ''The Divine Comedy'', the spirit of Solomon appears to Dante Alighieri in the Heaven of the Sun with other exemplars of inspired wisdom. * In Friedrich Dürrenmatt's ''Die Physiker'', the physicist Möbius claims that Solomon appears to him and dictates the "theory of all possible inventions" (based on ''Unified Field Theory''). * Solomon appears in Kipling's ''Just So Stories''. * In Neal Stephenson's three-volume ''The Baroque Cycle'', 17th-century alchemists like Isaac Newton believe that Solomon created a kind of "heavier" gold with mystical properties and that it was cached in the Solomon Islands where it was accidentally discovered by the crew of a wayward Spanish galleon. In the third volume of ''The Baroque Cycle, The System of the World'', a mysterious member of the entourage of Czar Peter I of Russia, named "Solomon Kohen, Kohan" appears in early 18th-century London. The czar, traveling incognito to purchase English-made ships for Imperial Russian Navy#Russian Navy during the reign of Peter the Great, his navy, explains that he added him to his court after the Azov campaigns#The second Azov campaign, Sack of Azov, where Kohan had been a guest of the Pasha. Solomon Kohan is later revealed as one of the extremely long-lived "Wise," such as Enoch Root, and compares a courtyard full of inventors' workstations to "an operation I used to have in Jerusalem a long time ago", denominating either facility as "a temple". Stephenson's sequel to ''Reamde'', 2019's ''Fall; or, Dodge in Hell'' was also a surprise sequel to the Baroque Cycle novels and ''Cryptonomicon''. In the mid- to late-21st century span of ''Fall'', Solomon Kohan has joined the faculty of Princeton University, going by ''Solly Pesador,'' and is described by a student as "one of those guys who had ''been around forever'' and played roles in tech companies going at least as far back as Hewlett-Packard" and as an "old-school tech geek turned neuro-hacker." * In ''The Ring of Solomon, Bartimaeus: The Ring of Solomon'', both King Solomon and the Queen of Sheba are featured prominently. * Solomon, King of Urushalim, is a significant character in ''The Shadow Prince'', the first novel of Philip Armstrong's epic historical fantasy, ''The Chronicles of Tupiluliuma''. His Ring is an Atalantaën Relic, by which is he able to command daemons. He uses it to summon a daemon army, thereafter called the Cohort of Free Daemons, to oppose the forces of the Chaos God, Sutekh, thus allowing the young Hittite musician, Lisarwa, to repair the Veil that separates the physical world from the dangerous wild energies of the Netherworld, using another of the relics, the Harp of Daud, once owned by his father (King David). Solomon's son,Film
* ''Solomon and Sheba'' (1959)—Epic film directed by King Vidor, starring Yul Brynner and Gina Lollobrigida * ''Solomon & Sheba (1995 film), Solomon & Sheba'' (1995)—Showtime film directed by Robert M. Young (director), Robert M. Young starring Halle Berry and Jimmy Smits * ''Solomon (film), Solomon'' (1997, TNT (U.S. TV network), TNT)—directed by Roger Young (director), Roger Young, starring Ben Cross * ''Brooklyn Babylon'' (2001)— a modern retelling of the story of Solomon and the Queen of Sheba, set during the Crown Heights riot * ''The Kingdom of Solomon (film), The Kingdom of Solomon'' (2009)—Iranian production directed by Shahriar Bahrani * ''The Song (2014 film), The Song'' (2014)—a modern retelling directed by Richard Ramsey, starring Alan Powell, Ali Faulkner, and Caitlin Nicol-ThomasMusic
* Giacomo Carissimi, ''The Judgment of Solomon'' for three chorus, two violins and organ * Marc-Antoine Charpentier, ''Judicium Salomnis,'' H 422, Oratorio for soloists, chorus, orchestra, and continuo 1702 * Sébastien de Brossard, ''Solomon's fall,'' cantata * George Frideric Handel, Handel composed an oratorio entitled ''Solomon (Handel), Solomon'' in 1748. The story follows the basic biblical plot. * Ernest Bloch composed a Hebraic Rhapsody for cello and orchestra entitled ''Schelomo'', based on King Solomon. * Kate Bush wrote a song called "Song of Solomon" in 1993 for her album ''The Red Shoes (Album), The Red Shoes''. * Toivo Tulev composed a piece for choir, soloists and chamber orchestra entitled ''Songs'' in 2005. The text is taken directly from the Song of Songs in its English, Spanish and Latin translations. * Derrick Harriott has a rocksteady song titled Solomon (later covered by Junior Murvin), in which he warns a woman that he is wiser than Solomon in the ways of women. * Jamaican dancehall rapper Sean Paul mentions King Solomon in his 2005 hit song "We Be Burnin". Specifically Sean Paul references the legend that marijuana was found on the grave of King Solomon. * The New Pornographers included a song entitled "One Kind of Solomon" on their 2019 album ''In the Morse Code of Brake Lights''. * Cassandra Wilson performs the self-penned 'Solomon Sang' on her 1995 Blue Note album, ''New Moon Daughter''. * Grateful Dead have a song called "King Solomon's Marbles" on their 1975 album, ''Blues for Allah''. *M. Nasir's "Tanya Sama Itu Hud Hud" revolves around the correspondence of the hoopoe (''hudhud'') with the figure especially as told through the poem ''The Conference of the Birds''. * Momus (musician), Momus' debut album Circus Maximus (Momus album), Circus Maximus featured a song called "King Solomon's Song And Mine". * The British Coronation Anthem "Zadok the Priest, Zadok The Priest" has a mention of a scene, in which King Solomon is anointed King by Zadok and Nathan the Prophet.See also
* Goetia * Heichal Shlomo * Kings of Israel and Judah * Solomon and Marcolf * Solomon in Islam * Solomon's Pools * Solomonic column * Solomonic dynasty * The Judgement of Salomon (Giorgione), ''The Judgement of Solomon'' (Giorgione) * Prison of Solomon * Takhte Soleyman, Throne of SolomonNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * *External links
* . * . * Animated depiction of the life of Solomon * Artistic movie about the rise and the reign of King Solomon * . * . , - {{Authority control Solomon, 10th-century BC biblical rulers 10th-century BCE Hebrew people 10th-century BC Kings of Israel (united monarchy) Books of Kings people Children of David Christian saints from the Old Testament Kings of ancient Israel Kings of ancient Judah People whose existence is disputed Wisdom Jewish royalty